Force-Controlled Ultrasound Scanning

In the case of high-tempo, traumatic scenarios on the battlefield, real-time ultrasound (US) imaging serves as an enabler for countless possible robotic interventions. Ultrasound has the benefit of being low-cost, portable, and radiation-free. The problem with ultrasound is that it is often difficult to interpret, therefore making interventions even more difficult, both for human caregivers and medical AI that supports them. This project aims to enable robotic-based ultrasound scanning with minimal human help. The challenge is divided into two parts:
- How to scan a curved/non-flat surface with proper ultrasound contact with the surface?
- How to find the best location/trajectory to scan given the target without human-in-loop?
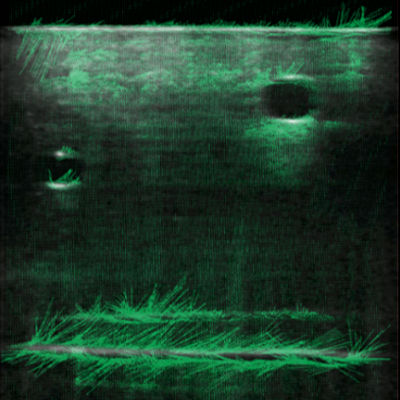
To solve the first question, we are looking to combine the force feedback with the prior knowledge of the surface to maintain maximum acoustic coupling and scan the target. We use commonly used metrics such as image noise and NCC score to quantify the scanning process. For the second part of the problem we are using Bayesian optimization to find the best location/trajectory on an unknown skin surface for needle insertion. Apart from the unknown surface geometry, other challenges in this include keeping the ultrasound normal to the surface to get a good image and using optimal force to press the probe on the surface such that the vessels don’t get deformed or injure the soldier. Furthermore, we are also working to create a simulation version of ultrasound scanning where we can test our algorithm in simulation before deploying on the real robot. The steps in this include a 3D volume reconstruction from ultrasound scans as well as pairing it with a physics engine for deformation modeling/control.